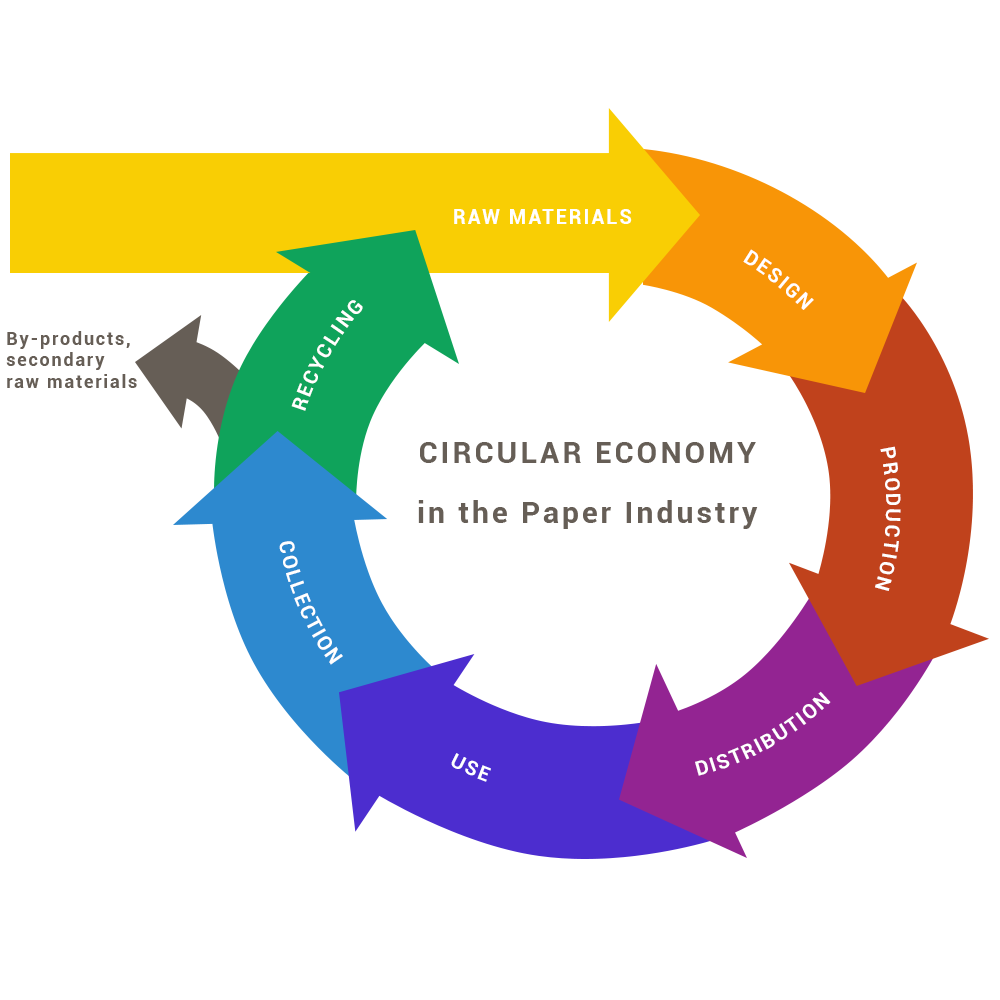
The paper industry has, through systematic efforts and investments, become a model of sustainable development in the industry in recent years. It does not endanger forests, as cellulose fibres are obtained from lower-quality wood or waste wood. For the production of paper and cardboard, it more or less uses cellulose with FSC or PEFC certification, which means it is obtained from a responsibly managed forest. The paper industry ranks among the most energy-efficient industries, contributing to a more balanced greenhouse gas emissions profile. With efficient modern technologies, paper mills have managed to reduce the consumption of water resources despite increased production. Thanks to efficient treatment plants, the "borrowed" water is returned to nature in an even cleaner state.
Recycling waste paper and cardboard is ecologically beneficial mainly because of the sensible use of natural resources. Paper reconditioning is a demanding process that is not environmentally friendly. The removal of printing inks through the deinking process is particularly challenging, as it requires significant energy and chemical input. Cellulose fibres can be recycled more than 25 times. Through repeated processing of the cellulose fibre, the fibre is damaged, so a certain proportion of fresh fibres is added to maintain the desired physical properties of paper and cardboard. Recycled fibres cannot be used to reproduce paper or cardboard of the same quality but are used to produce a lower quality grade than the original. It should be emphasized that cellulose fibres do not represent a foreign body for the environment even after the end of their useful life, and they decompose by themselves in nature.










